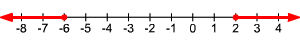Absolute Value Inequalities
An absolute value inequality is an inequality that has an absolute value sign with a variable inside.
Absolute Value Inequalities ( ):
The inequality means that the distance between and is less than .
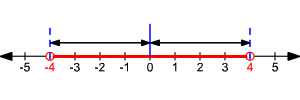
So, AND . The solution set is .
When solving absolute value inequalities, there are two cases to consider.
Case : The expression inside the absolute value symbols is positive.
Case : The expression inside the absolute value symbols is negative.
The solution is the intersection of the solutions of these two cases.
In other words, for any real numbers and , if , then AND .
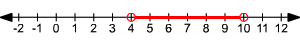
Example 1 :
Solve and graph.
To solve this sort of inequality, we need to break it into a compound inequality .
and .
Add to each expression.
The graph looks like this:
Absolute Value Inequalities ( ):
The inequality means that the distance between and is greater than .
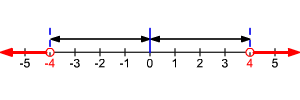
So, OR . The solution set is .
When solving absolute value inequalities, there are two cases to consider.
Case : The expression inside the absolute value symbols is positive.
Case : The expression inside the absolute value symbols is negative.In other words, for any real numbers and , if , then AND .
Example 2 :
Solve and graph.
Split into two inequalities.
Subtract from each sides of each inequality.
The graph looks like this: